While AI technologies and their application via chatbots, AI-generated content, or increase in data driven campaigning enhanced voter engagement and campaign efficiency in India's 2024 elections, their dual capability for both democratic enablement and manipulation highlights urgent needs for regulatory frameworks to protect electoral integrity in the digital age.
The paper explores how Artificial Intelligence (AI) was utilized in the 2024 general elections in India, a year marked by a significant increase in the use of technology in political campaigns. The widespread use of AI tools globally during the “super election year,” a term coined by the UNDP, raised questions about their impact on democratic processes. In the Indian elections, key applications included deepfake technology, targeted voter outreach, and AI-generated campaign materials. AI was employed both positively – enhancing the effectiveness of campaign outreach and enabling customized messaging – and negatively, allowing campaigners to amplify propaganda and spread deceptive content and misinformation to the masses, which was not possible in previous election campaigns.
This text was first published by Friedrich-Naumann-Foundation. You can read the full Policy Paper by D Dhanuraj, Sreelakshmi Harilal, and Nissy Solomon here.
Explore the Data
AI-Incidents:
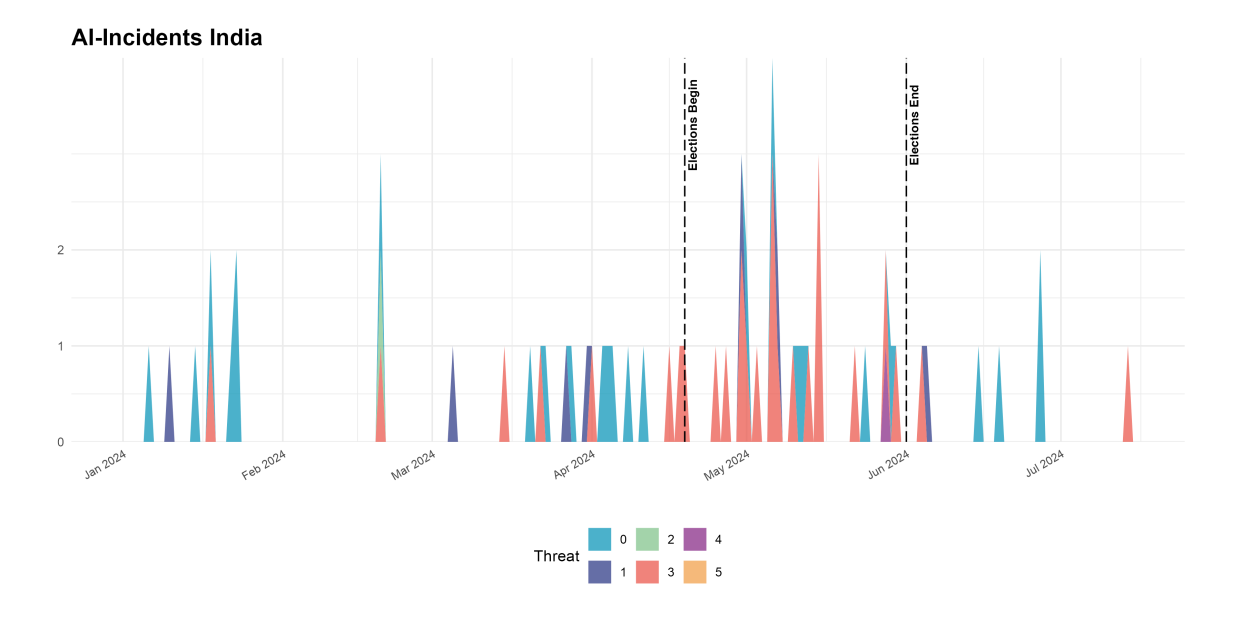
India's General Elections took place from April 19 to June 1, 2024. Our analysis of AI-related incidents during this period, spanning January 1 to June 30, 2024, reviewed 1,536 news articles and uncovered 62 unique AI-related cases.
Trends:
- Personalized messaging and microtargeting of voters with the help of AI
-
Political parties used AI to target voters with personalized messages via WhatsApp.
- AI used as a translation tool, fostering widespread accessibility of political campaigns
-
Narendra Modi used AI as a real-time translation tool, enabling him to reach a wider audience.
- Convergence of traditional campaign methods with AI
-
AI enabled the seamless integration of traditional campaigning methods with modern technology.
- AI as an Equalizer in Elections
-
Smaller parties were able to run large-scale campaigns, thanks to the cost efficiency of AI tools.
- High Levels of Misinformation Exposure, with AI-Generated Content on the Rise
-
AI-generated misinformation campaigns significantly increased during the election period.
Proxy Variables:
- Trust in News
- Source of News
- Social Media Usage
- Trust in Media and Government
Vulnerabilities:
- Large-Scale Data Collection Used for Profiling of Voters
-
A central feature of Indian campaigning was data collection, leading to hyper-personalization of political communication. This practice may lead to polarization and voter manipulation.
- AI Detection Challenges of Localized Misinformation
-
Misinformation is often distributed locally in regional languages, creating significant challenges for fact-checking and automated detection systems.